first step of purine metabolism is to create PRPP which stand for 5 phosphoribosyl 1 pyrophosphate
from ribose 5 phosphate.
the second step is : glutamine + PRPP → phosphoribosylamide
the amide group is replaced from glutamine to PRPP
the enzyme catalyze this step is glutamine :phosphoribosylamidotransferase GPTA which is rate limiting step for purine synthesis this enzyme is inhibited by final products of purines pathway AMP GMP the rate of this reaction is also controlled by intracellular concentration of PRPP because its concentration is normally below michaelis constant or km therefore any small change in the PRPP concentration causes proportional change in the rate of reaction.
next step is to create IMP whose base is hypzanthine and it is the parent nucleotide for AMP and GMP it's found in tRNA.
drugs that related to this step: ribavirin (antiviral)
inhibit IMP dehydrogenase which means it cut the metabolism way and prevent conversion of IMP to GMP as a result all the purines are inhibited.
ribonucleotides are synthezied first then converted to deoxyribonucleotides by an enzyme called ribonucleotide reductase which is composed of two nonidentical subunits R1 and R2, the immediate donors of the hydrogen atoms needed for the reduction of the 2 hydroxyl group are two sulfhydryl (sh) group on the enzyme R1 unit.
purine salvage : means converting purines from diet or result from normal turn over back into nucleoside triphosphate.
this requires PRPP because it looks like a nucleotide but without a base and three phosphate so if you put your base and took the phosphate you will have a new nucleotide, the enzyme that catalyze this step for hypoxanthine and guanine is called HGPRT stand for hypoxanthine - guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. but for the adenine has its own enzyme which called APRT.
drugs related to purine salvage : 6 mercatoprine 6MP: which is chemotherapy agent mimics hypoxanthine and guanine so the HGPRT will think it is them and combine to them and result in structure called thioinosonic acid which is obvisouly cut the salvage way and inhibit multiple steps in de novo synthesis result in decrease amount of IMP GMP AMP.
Azathioprine : this one is immunosuppressant and converted inside the body to 6MP.
purines breakdown: hypoxanthine and guanine to uric acid as final product as shown in the figure below
while adenine breakdown is just little more complicated as shown in the figure
SCID stand for severe compined immuno deficiency syndrome which adenosine deaminase dificiency... well not our concern right now
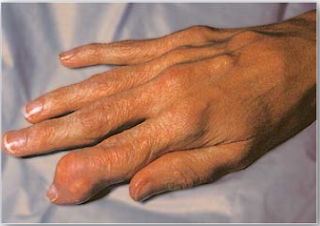
diseases related to purine breakdown : Gout : excess uric acid in blood which may look like hyperuricemia as either of them result in excess uric acid in blood the hyperuricemia can lead to deposition of monosodium urate crystals in joints, symptoms are pain, swelling and redness in joints usually result from overproduction or underexcretion or just a lot consumption of purine rich food after a big meal, the definite diagnosis of Gout which can tell you is hyperuricemia or Gout is examination of synovial fluid from an affected joint using polarized light microscope to confirm the presence of needle shaped MSU crystals. remember Hyperuricemia is not sufficent to cause Gout but gout is always preceds with hyperuricemia.
treatment : acut attacks of gout are treated with Colchicine, prednisone and indomethacin. notice that these drugs prevent formation of microtubules thereby decrease the movements of neutrophils in affected joint and has no effect at uric acid levels, while long term theraputic stratiges involve lowering the level of uric acid below its saturation point these drugs are Probenecide or sulfinpyrazone, that increase renal excretion of uric acid. And allopurinol is used for overproducers because it inhibit xanthine oxidase.
gout patients may look like this
but you must be careful when you describe allopurinol because 6 MP and azathioprine and metabolized by xanthine oxidase too so when you describe allopurinol allong with them this will boost their effect and it may be toxic but sometimes you may need to boost their effect on purpose.
lesh-Nyhan syndrome : this rare X linked recessive disorer associated with complete absence for HGPRT which cut the salvage pathway for sure and the lack of this pathway causes increased PRPP levels and decreased IMP and GMP levls as result GPAT has excess substrate and decreased inhibitors then the de novo purine synthesis is incresed and without salvage it is all going to turin into uric acid which cause hypernuricemia. the child will have self mutilation (bitting or scratching) hypotonia, chorea and there is no treatment sadlly.
reference I used is lippincot and some online lectures
this is my first day please drop your opinons down the comments and how good or even bad you think I was ? 😂 and thanks








No comments:
Post a Comment